(+86)0532-88988868
pH meter is a commonly used instrument and equipment, mainly used to accurately measure the pH of liquid medium, if equipped with the corresponding ion selection electrode can also be used to measure the ion electrode potential value, widely used in industry, agriculture, scientific research and environmental protection fields.
Classification of pH meters
According to the different measurement methods, pH is divided into indicator method, hydrogen electrode method, hydroquinone electrode method, antimony electrode method, and glass electrode method.
At present, the most widely used is the glass electrode method, which is mainly divided into two forms, namely the traditional glass electrode, the reference electrode, and the composite electrode that combines the two.
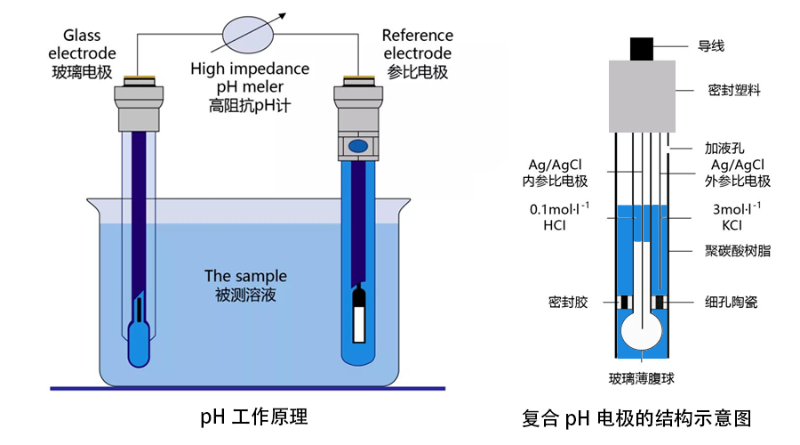
Here is a brief explanation of the principle of a glass electrode pH meter: if there is a glass film between two solutions with different pH, then across the glass film will produce a potential difference, which is proportional to the difference in pH of the two solutions.
When determining the pH of a solution, a set of glass electrodes and a reference electrode are placed in both the solution to be measured. The glass electrode is sensitive to pH, and the reference electrode is stable potential, and the two constitute a galvanic cell in the measured solution, and the potential of the galvanic cell is the algebraic sum of the potentials of the glass electrode and the reference electrode.
Therefore, when the temperature remains stable, the potential change of the galvanic cell is only related to the potential of the glass electrode, which depends on the pH of the solution being measured.
So by measuring the change in potential, the pH value of the pH solution can be obtained.
Composite electrodes are commonly used today, some with temperature compensation, which makes the measurement results more accurate.
Selection and precautions of pH meter
At present, glass electrode pH meters and differential electrode pH meters (pH/ORP) are commonly used.
Glass electrode pH meters are divided into portable glass electrode pH meters and online glass pH meters, which are suitable for corresponding needs.
The following precautions need to be taken when using the glass electrode pH meter:
The glass electrode socket should be kept dry and clean, and it is strictly forbidden to contact with harmful gases such as acid mist and salt spray, and it is strictly forbidden to be stained with aqueous solution to ensure the high input impedance of the instrument;
New or long-lived electrodes must be soaked in distilled water for several hours before use. The asymmetric potential of the electrode is reduced to a stable level, and the internal resistance of the electrode is reduced.
When measuring, the electrode bulb should be fully immersed in the solution to be measured;
When using, the reference electrode should be removed and the rubber plug at the liquid filling port should be removed, so that the reference electrolyte (salt bridge) can maintain a certain flow rate by gravity and communicate with the measured solution, so as not to cause reading drift.
Differential pH/ORP uses a technique of differential electrode measurement (e.g., US hash), which uses three measuring electrodes instead of two electrodes in a conventional pH sensor, and the measured value is obtained by measuring two glass electrodes relative to the differential value of the third metal electrode. Contamination of the reference electrode connection is reduced and accuracy is improved.
The above is a brief introduction to the pH meter, and you can consult the instructions and operation manuals of the corresponding pH meter by yourself.


