Marketing Hotline:
(+86)0532-88988868
(+86)0532-88988868
1 Flocculation principle.
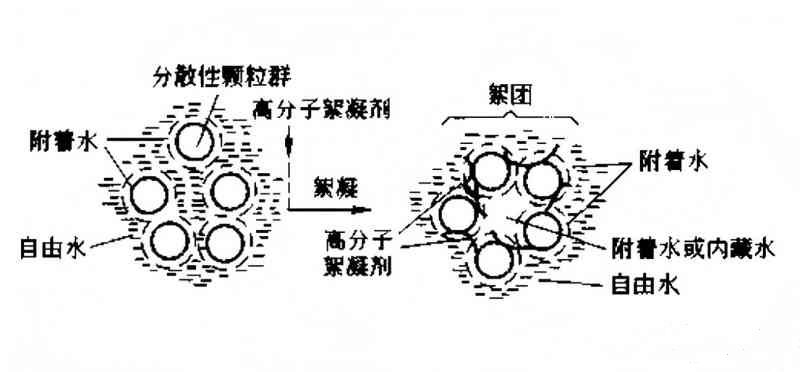
The quality of fine suspended particles and colloidal particles in wastewater is relatively light, especially the diameter of colloidal particles is 10--³~10-⁸ mm, because these fine particles do irregular Brownian motion in water, and colloidal particles have the same charge, there is electrostatic repulsion between each other, so they can not be close to each other to form larger particles and sink. As a result, the fine suspended particles and colloidal particles in the wastewater are not easy to settle and always remain dispersed and relatively stable. Therefore, in order to make colloidal particles settle, it is necessary to destroy the stability of colloidal particles and promote colloidal particles to contact each other to become larger particles, and the key is to reduce the charge of colloidal particles. Coagulation is a general term for coagulation and flocculation. Coagulation refers to the addition of low-molecular weight electrolytes and colloidal particles to the charge of sewage, reducing the potential and destabilizing the colloid. Flocculation refers to the addition of a small amount of polymer to the sewage, the polymer molecules are quickly adsorbed and combined on the surface of colloidal particles, a polymer chain can adsorb multiple colloidal particles at the same time, and each particle relies on polymer linkage to form a certain aggregate or combine into flocculent and precipitate and separate.
In fact, the two are not separated in the wastewater coagulation process. The comprehensive process of adding chemicals to wastewater and mixing water and chemicals to produce agglomeration and flocculation of colloidal substances in water is called coagulation process.
2. Influencing factors of flocculation
Factors influencing coagulation include pH, temperature, coagulant, and agitation. The substance that can make colloidal particles in water stick and coalesce with each other is called coagulant, which has the function of destroying colloidal stability and promoting colloidal flocculation.
3. The role of flocculation

Coagulants can usually be divided into two categories: inorganic salts and polymers. Inorganic salts include coagulants such as aluminum sulfate, alum, and ferric chloride; Polymers include polyaluminum chloride, polyferric chloride, etc.
Dosing coagulation treatment can effectively reduce the turbidity and color of wastewater, and remove colloidal polymer organic substances, radioactive substances and other fine particulate substances in wastewater. In the actual wastewater treatment process, sometimes a single coagulant can not achieve good results, and it is often necessary to add auxiliary agents to improve the coagulation effect, which is called coagulant. In addition, in order to strengthen the sedimentation effect of the sedimentation tank, the coagulation method is also commonly used in the primary sedimentation tank and the secondary sedimentation tank, and the coagulation process is also commonly used when the secondary effluent is treated for tertiary or advanced treatment.


